1. Figure 구성요소 (Parts of a Figure)

Figure
Figure: 전체적인 그림을 가리킨다. pyplot을 이용하여 만들 수 있다.
fig = plt.figure() # 축이 없는 빈 figure를 생성한다.
fig, ax = plt.subplots() # Axes 하나인 figure를 생성한다.
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2) # 2x2 그리드인 figure를 생성한다.Axes
Axes: plot(도표) 이라고 생각하는 것이며, 데이터 공간을 가진 이미지 영역이다. figure는 다수의 Axes를 포함할 수 있지만, Axes 는 2차원 그래프의 경우 데이터 한계를 처리하는 2개의 Axis 오브젝트를 포함한다. 각각의 Axes는 title 과 x-label, y-label을 가진다.
methods
axes.Axes.set_xlim(): x축 한계 설정axes.Axes.set_ylim(): y축 한계 설정set_title(): 제목 설정set_xlabel(): x축 라벨 설정set_ylabel(): y축 라벨 설정
Axis
Axis: number-line-like 오브젝트이다. graph 제한이나 ticks (축 위의 마크: 눈금), ticklabels (눈금 표시 문자열 라벨)을 세팅할 수 있다.
ticks의 위치는 Locator 오브젝트에 의해 결정되고 ticklabels은 Formatter 오브젝트로 포매팅된다. Locator과 Formatter를 적절히 자용하여 ticks와 ticklabels를 세밀하게 제어할 수 있다.
Artist
Artist: 기본적으로 도표 (figure)에서 볼 수 있는 모든 것은 Artist이다 (Figure, Axes, Axis, ...). Artist는 Text, Line2D, collections, Patch 등의 오브젝트를 포함한다. figure가 렌더링되면 모든 artist는 canvas에 그려진다. 대부분의 Artist는 Axes에 연결되어 있으며 이러한 Artist는 여러 Axes에서 공유하거나 다른 Axes로 이동할 수 없다.
2. plotting 함수의 입력 타입 (Types of inputs to plotting functions)
plotting 함수는 입력으로 numpy.array 또는 numpy.ma.masked_array를 받는다. pandas 데이터 오브젝트나 (ex. DataFrame) numpy.matrix는 동작하지 않을 수도 있다. 함수를 사용하려면, numpy.array 로 변환하는 것을 가장 권장하고 있다.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# pandas.DataFrame to numpy.array
a = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(4, 5), columns=list('abcde'))
a_array = a.values
# numpy.matrix to numpy.array
b = np.matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b_array = np.asarray(b)3. object-oriented 인터페이스와 pyplot 인터페이스
matplotlib는 동일한 성능을 내는 object-oriented (OO-style) 인터페이스와 pyplot 인터페이스 2개의 방법을 사용하여 figure를 그린다.
object-oriented: 인터페이스를 사용하면 그림과 축을 명시적으로 만들고, 그 위에 메소드를 호출한다.pyplot: 그림과 축을 자동으로 생성하고 관리하며,pyplot함수를 사용하여 플로팅을 한다.
pylab import *를 사용하여 pylab 인터페이스를 사용하는 예제를 확인할 수도 있는데 이것은 MATLAB-like style이며 이전에 사용하던 사용 방법이다.
3.1. object-oriented 인터페이스
- 그림과 축을 명시적으로 만들고, 그 위에 메소드를 호출한다.
- non-interactive style (대규모 프로젝트의 일부로 재사용될 수 있는 function 과 script)에 적합하다.
ex-1
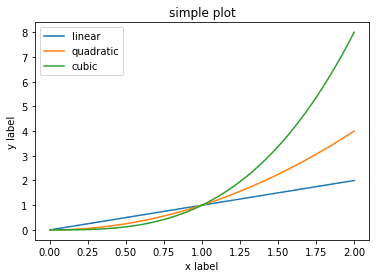
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 2, 100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots() # figure와 axes를 생성한다.
ax.plot(x, x, label='linear') # 데이터를 axes에 그린다.
ax.plot(x, x**2, label='quadratic') # 다른 데이터를 axes에 그린다.
ax.plot(x, x**3, label='cubic')
ax.set_xlabel('x label') # axes의 x축에 label을 추가한다. (add x-label)
ax.set_ylabel('y label') # axes의 y축에 label을 추가한다. (add y-label)
ax.set_title('simple plot') # axes에 title을 추가한다.
ax.legend() # legend를 추가한다.
plt.figure() # figure를 그린다.ex-2
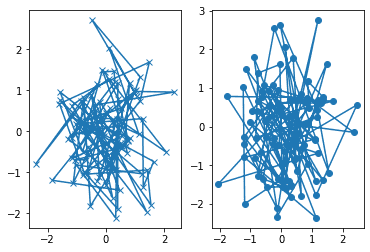
def my_plotter(ax, data1, data2, param_dict):
"""
A helper function to make a graph
Parameters
----------
ax : Axes
The axes to draw to
data1 : array
The x data
data2 : array
The y data
param_dict : dict
Dictionary of kwargs to pass to ax.plot
Returns
-------
out : list
list of artists added
"""
out = ax.plot(data1, data2, **param_dict)
return out
data1, data2, data3, data4 = np.random.randn(4, 100)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
my_plotter(ax1, data1, data2, {'marker': 'x'})
my_plotter(ax2, data3, data4, {'marker': 'o'})3.2. pyplot function
- 그림과 축을 자동으로 생성하고 관리하며, pyplot함수를 사용하여 플로팅을 한다.
- interactive plotting (ex, jupyter notebook) 에 더 적합하다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 2, 100)
plt.plot(x, x, label='linear') # axes 위에 데이터를 표시한다.
plt.plot(x, x**2, label='quadratic') # 위와 같음
plt.plot(x, x**3, label='cubic') # ...
plt.xlabel('x label') # x 축에 라벨을 추가한다.
plt.ylabel('y label') # y 축에 라벨을 추가한다.
plt.title("Simple Plot") # 제목을 추가한다.
plt.legend() # legend 를 추가한다.
plt.figure()